Methylcycle
TM
Methylation support: Beyond folate 5-MTHF is reduced in the folate cycle, impacting methionine in the methylation cycle where SAMe is reduced to homocysteine, donating a methyl group. Homocysteine can be recycled to methionine and SAMe with available folate and B12 resources. If resources are deficient, homocysteine enters an alternate path dependent on choline or trimethylglycine (TMG) availability. Transsulfuration occurs when methylation needs are met. SAMe upregulates enzymatic activity converting homocysteine to internal antioxidant glutathione and ATP supporting pyruvate. Methyl FMT provides key precursor support and complete enzymatic cofactor coverage for the FMT pathways, targeting methylation to homocysteine1-5*
Rapid rise and decline in cortisol after stress is considered a healthy response and desirable dynamic, adaptive response. Conversely, changes in cortisol stress reactivity marks susceptibility for systemic complications and can be impacted by internal and external factors6* Exposure to stressors/trauma can impact DNA methylation that is functionally relevant for stress programming in the human brain6* Methylation is associated with balanced cortisol stress reactivity6
Folate and B12 availability determine how oxidative stress and cardiovascular marker homocysteine is recycled in a healthy methylation pathway.*The folate cycle impacts biopterin, required for hydroxylase enzymes involved in serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine production, impacting a variety of occasional symptoms such as mood, cravings, cognition, temperature regulation, and immune activity.7-11*Methylation, or SAMe, is required for epinephrine and melatonin production, impacting energy, endurance, motivation, and the sleep wake cycle.7-10*
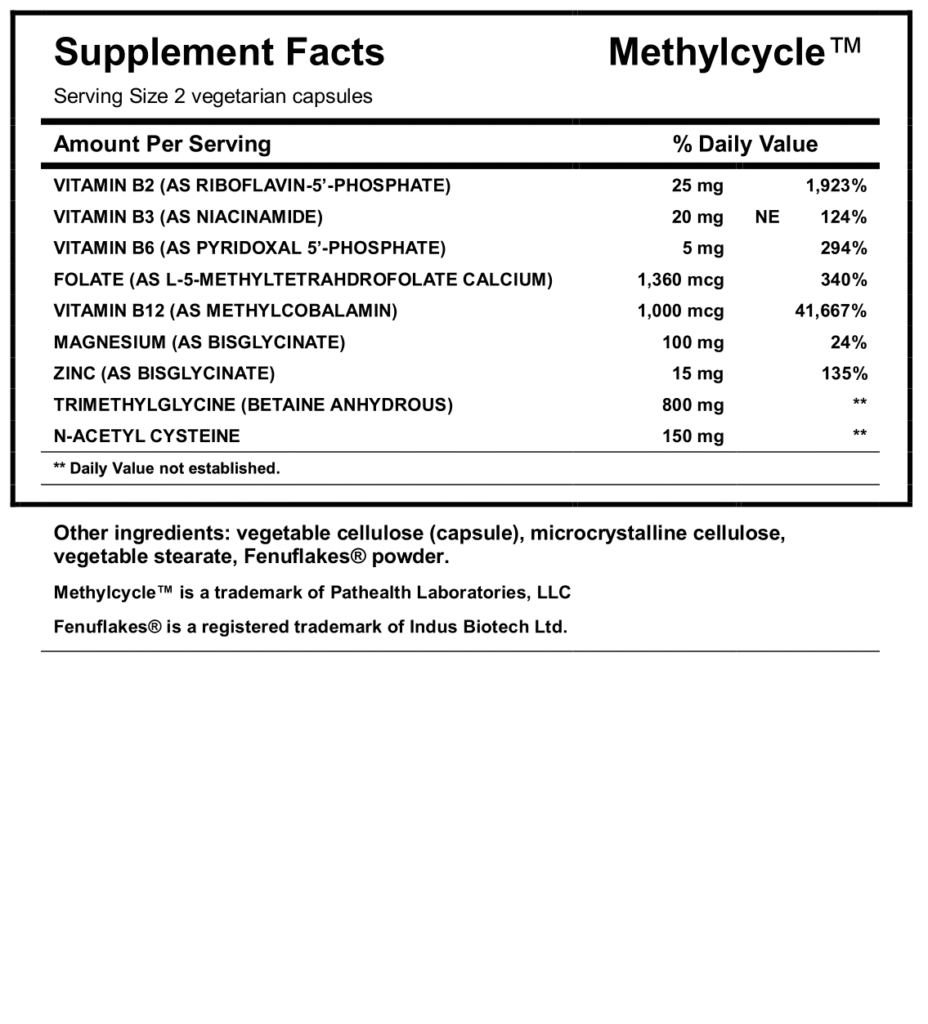
Vitamin B2, essential for MTHFR and MTRR coenzyme FAD in the folate cycle Riboflavin supplementation has been shown to reduce homocysteine activity in those with genetic predisposition1
Niacin, in the form of NAD, is a necessary cofactor for the enzymes DHFR in the folate/tetrahydrobiopterin cycles and S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase in the methionine cycle2
Vitamin B6, essential cofactor for multiple enzymes in the methylation and transsulfuration pathways including SHMT, CBS, and CTH3,4 Essential cofactor for synthesis of neurotransmitters such as dopamine, GABA, norepinephrine, epinephrine, and serotonin
L-5-MTHF, primary form of folate used by the body; does not require metabolism for absorption Patented crystallization form for preferred stability*‡
Vitamin B12, essential cofactor for the metabolism of L-5-MTHF in the folate pathway and homocysteine activity in the methionine pathway
Magnesium, special form of magnesium bound to glycine molecules naturally creating a low weight chelate with enhanced bioavailability**. Required cofactor for methionine adenosyl-transferase, the enzyme responsible for synthesizing SAMe in the methionine pathway
Zinc, essential cofactor enzymes in the methylation pathway including MTR and BHMT
Trimethylglycine, potent methyl donor and substrate for BHMT, sparing choline resources* Trimethylglycine supplementation has been shown to support healthy homocysteine levels5
- McNulty H, et al. Circulation. 2006;113:74-80.
- Kennedy D. Nutrients 2016, 8, 68.
- Perry C, et al. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2007;462(1):21-27.
- Gregory J, et al. Biochimie. 2016;126:21-26.
- Olthof M, et al. J Nutr. 2003;133(12):4135-8.
- Houtepen L, et al. Nat Commun. 2016;7:10967.
- BlierP. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2001;26 Suppl:S1-2.
- Clark K and Noudoost B. Front Neural Circuits. 2014;8:33.
- Verhoeff N, et al. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2003;74(2):425-32.
- Xing B, et al. Brain Res. 2016;1641( Pt B):217-33.
- Bardin L. Behav Pharmacol. 2011;22(5-6):390-404.
N-acetylcysteine (NAC) does not directly add methyl groups to DNA (DNA methylation), but it can influence methylation indirectly. NAC supports methylation by reducing homocysteine and boosting glutathione production, both of which play supporting roles in methylation pathways. It can also reverse the negative effects of certain nanoparticles on DNA methylation.
Here’s a more detailed explanation:
NAC and Methylation Pathways:
NAC helps convert homocysteine into cysteine and other compounds, thus reducing homocysteine levels. High homocysteine can interfere with methylation.
NAC is a precursor to glutathione, a powerful antioxidant. Glutathione helps protect cells from oxidative stress, which can negatively impact methylation processes.
Studies have shown that NAC can reverse the decrease in DNA methylation status caused by certain nanoparticles.
N-acetyl-cysteine supplementation lowers high homocysteine plasma levels and increases glutathione synthesis in the transsulfuration pathway. Beneficial effects on several cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases
Federico Cacciapuoti
DOI: 10.4081/itjm.2019.1192
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.